Overview
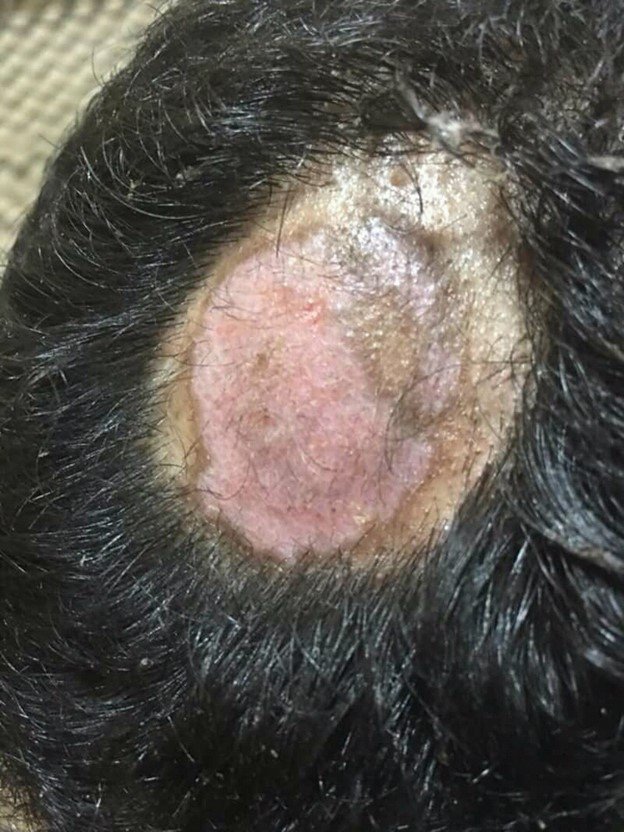
Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and scarring on the skin. DLE typically affects the face, scalp, and neck, but can occur anywhere on the body. The cause of discoid lupus is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The diagnosis of discoid lupus is based on your symptoms and physical examination. There is no cure for discoid lupus, but treatment can help reduce inflammation and improve symptoms. Most people with discoid lupus have a good prognosis and go into remission after treatment.
What is the cause of discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE)?
Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and scarring on the skin. The cause of discoid lupus is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
What are the symptoms of discoid lupus?
DLE typically affects the face, scalp, and neck, but can occur anywhere on the body. The most common symptom of discoid lupus is a rash that appears as red or purplish patches on the skin. These patches may be scaly or crusted. Discoid lupus can also cause hair loss, especially on the scalp. Discoid lupus may also cause other less common symptoms, such as:
- fatigue
- joint pain
- fever
- weight loss
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Discoid_lupus_etythermayouses_new_image.jpg
License: Mohammad2018, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
How is discoid lupus diagnosed?
The diagnosis of discoid lupus is based on your symptoms and physical examination. Your doctor may also recommend a biopsy, which is a procedure to remove a small piece of skin to be examined under a microscope. A biopsy can help confirm the diagnosis of discoid lupus.
How is discoid lupus treated?
There is no cure for discoid lupus, but treatment can help reduce inflammation and improve symptoms. Treatment for discoid lupus may include:
- topical and oral corticosteroids
- antimalarial medication
- immunosuppressive drugs
Most people with discoid lupus have a good prognosis and go into remission after treatment. However, discoid lupus can come back, and some people may develop systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), which is a more serious form of the disease. If you have discoid lupus, it is important to see your doctor for regular checkups and to report any new symptoms.